Solution overview
The previous page outlines the challenges encountered as organizations transform to become data-driven. The roadmap for development of Hackolade Studio features are centered around capabilities that address these challenges.
Having witnessed these patterns at many of our customers, whether small, medium, or large, our mission was developed to restore the collaboration between business and IT while operating in an increasingly complex technical environment. The vision leverages data modeling to establish the bridge between the respective and preferred metadata repositories of each community, and to make data architects and data modelers facilitate the collaboration between all the data stakeholders in the organization. This can be accomplished without falling into the extremes of gigantic enterprise data models that get in the way of getting things done.
Data modeling is not a goal in and of itself. Hackolade Studio, our next-gen data modeling tool, provides the solution as a means to an end.
At a tactical level, data modeling serves a design purpose -- the design of data structures used in databases and data exchanges -- and a communication purpose -- the collaborative discussion of these structures between the different stakeholders of data, whether they are from the technical side of the organization, or the business side.
At a more strategic level, the purpose of data modeling is therefore to

When business and IT don't work hand-in-hand on projects, the vocabulary diverges, and so does the understanding of the domain and the business objectives of initiatives. In the end, not only budgets explode and deadlines are missed, but there's a misunderstanding of the data itself, which can easily lead to bad business decisions and AI hallucinations.
The slide below outlines the mapping of our solution and resulting business outcomes to the defined challenges.
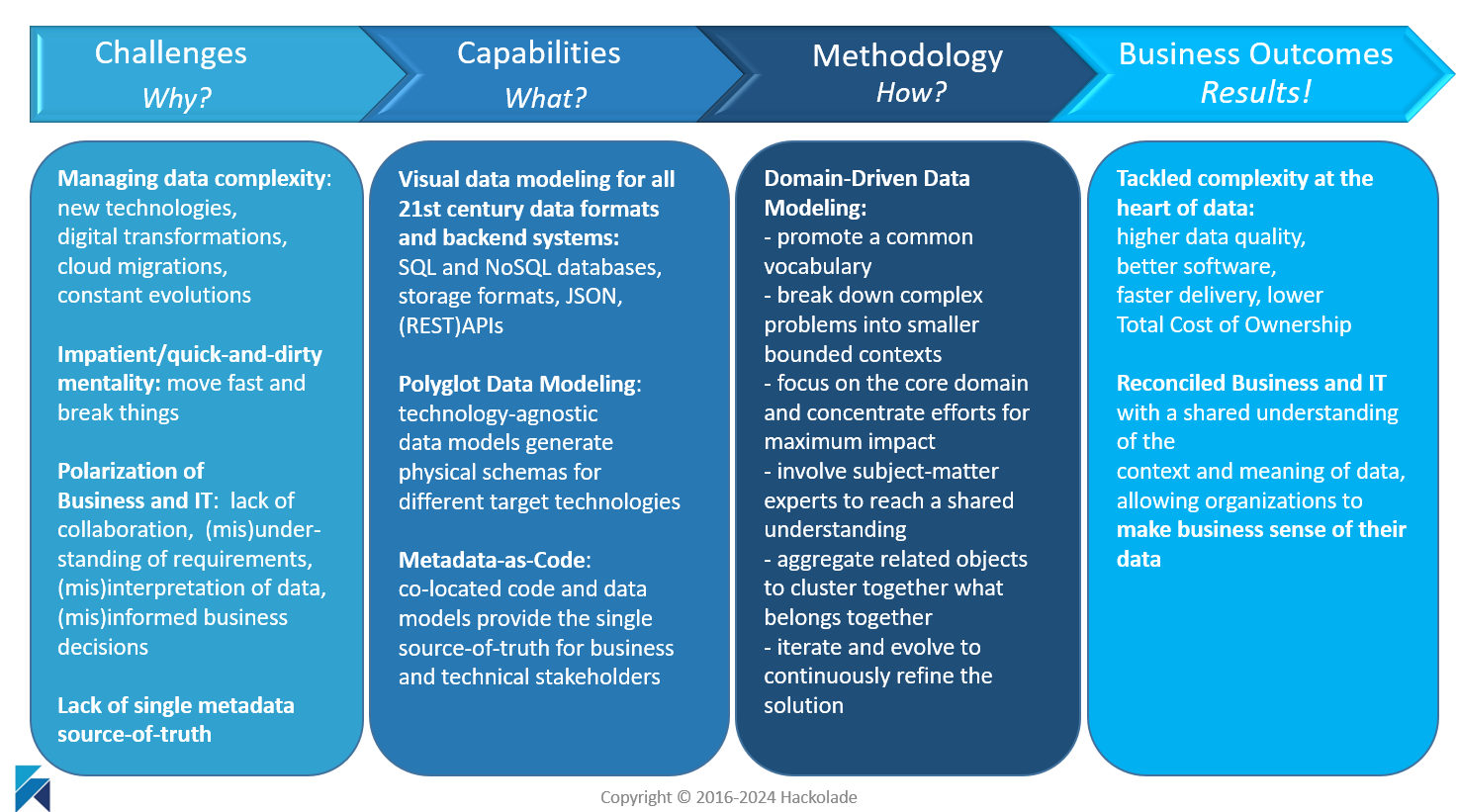
Next-gen data modeling
Across all industries, everyone agrees when talking about quality: the sooner a defect is detected, the cheaper it is to correct it. Data is no exception.
Building architects use AutoCAD to create the blueprint for a construction, so they can discuss vision and details with the owner or real estate developer, contractors, engineers, surveyors, inspectors, etc.. Blueprints are detailed technical drawings that provide a clear visual representation of the project, that convey the architectural and engineering design of the structure, and help help everyone understand the layout and specification.
The lack of a blueprint can lead to all kinds of challenges: design errors, construction errors, disagreement and disputes, inefficiencies, delays, cost overruns, increased cost for changes, difficulty in future maintenance and renovation, safety concerns, regulatory non-compliance, etc. Except for maybe building a shed in the backyard, no one would imagine to embark on the construction of any kind of complex structure without having a blueprint to discuss and agree on.
Databases and data exchanges are becoming increasingly complex as organizations ambition to become more data-driven. Data, and the ability to make sense of it, has been one of the greatest drivers of innovation in organizations and society in recent decades, and a primary driver of economic success in the 21st century. But the risk, if we lose sight of what data actually means, is that we end up with hallucinations (in the case of AI) and bad decisions (in the case of reporting and analytics.)
Data architects play a critical role in designing and managing an organization's data infrastructure to ensure that data is collected, stored, processed, used effectively, and correctly interpreted to support business goals. Data architects use Hackolade Studio to create data models, a visual representation for the data structures at the core of software applications.
Data models are blueprints for data structures and serve as a communication tool. They are used to convey the design of the structure of data so the vision and details can be discussed by all the stakeholders of applications: subject-matter experts, analysts, architects, designers, developers, testers, DBAs, etc.. The data modeling exercise is an opportunity for business and IT to closely collaborate on a shared understanding while working hand-in-hand. Data modeling is a proactive process that involves designing data structures before data is created or collected. It allows organizations to anticipate their data needs and ensure that data is structured optimally from the start.
To create a visual representation of data structures, data modeling tools have traditionally been using Entity-Relationship Diagrams. Hackolade has enhanced traditional ERDs with a patented ability to represent nested objects and complex data types, and with the ability to represent the structure of graph databases.
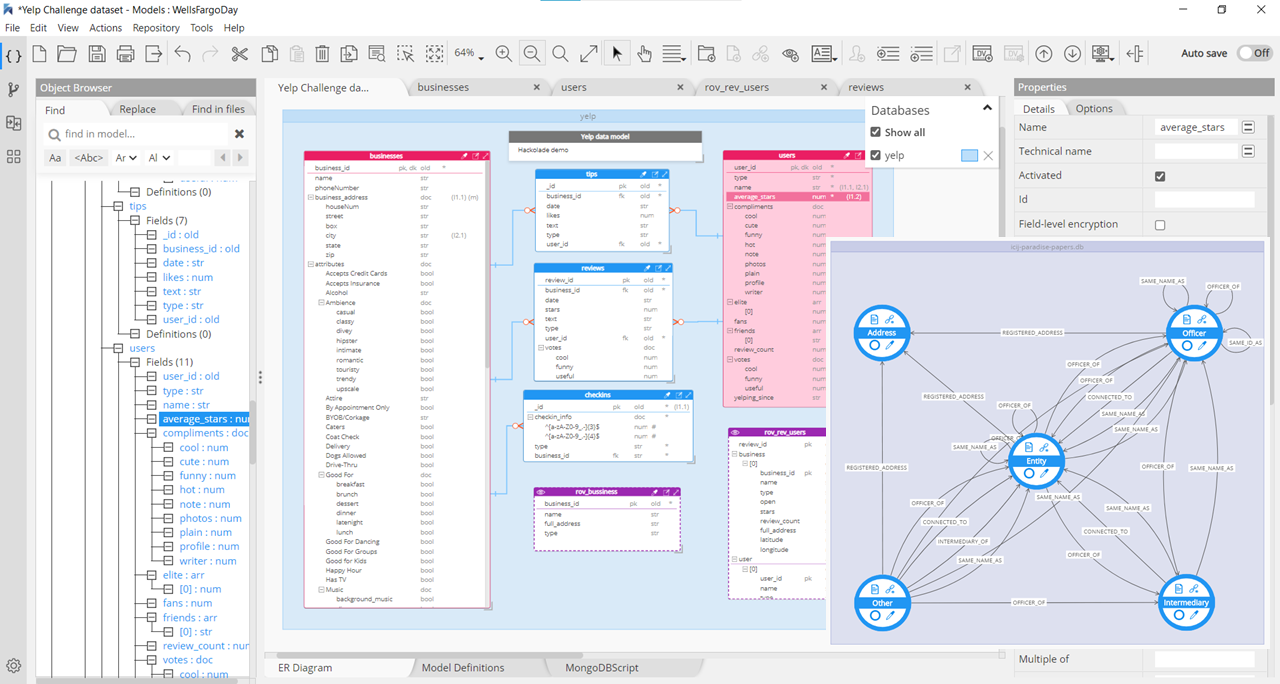
While data dictionaries, business glossaries, metadata management and data governance solutions do a good job of cataloging data after the fact, they're missing a critical piece of the equation: the design phase of data structures. When these tools discover data structures and expose them to data citizens, often times, the damage is done already. Data is being accumulated in ambiguous or just wrong structure and metrics. Data modeling should take place upstream in the development process and ensures that data is stored correctly and according to the needs of the business as identified by subject matter experts of each domain.
Polyglot Data Modeling
Data modeling is traditionally made of 3 levels: conceptual, logical, and physical. The Conceptual data model is defined as a high-level description of the informational needs underlying the design of a database, typically including only the main concepts and the main relationships among them. A Logical data model is a technology-agnostic expression of the data structures, capturing the business rules and constraints for the data. Whereas a Physical data model is a representation of a data design as (intended to be) implemented in a database management system.
Although this is sometimes subject to interpretation, logical data models are supposed to be strictly normalized and to use only scalar data types. These constraints directly contradict the main characteristic according to which logical models must be technology-agnostic. The problem is that they can only be technology-agnostic if, and only if, the target technology is a relational database, thereby excluding any modern technology that is more flexible and powerful. Converting a technology-agnostic logical model into the different dialects of SQL for RDBMS is relatively easy, and all the legacy data modeling tools can do it. But it is much harder to abstract the capabilities and understand the syntax of each modern technology, and be able to define a technology-agnostic data model that also allows denormalization and complex data types.
As a result, and to avoid any confusion, our implementation of logical data models bears a different name: "polyglot", to reflect the fact that it is truly technology-agnostic, i.e.: not limited to relational databases. Our Polyglot Data Model is not limited by the constraints of normalization and scalar data types since it supports hierarchical structures, with objects and arrays, as well as denormalization.
Polyglot data modeling is data modeling for polyglot persistence and data exchanges. The term polyglot simply means that organizations are storing and exchanging data using a variety of technologies "speaking different languages." This highlights the unique capability of Hackolade Studio to "speak" all these different languages -- not just SQL for RDBMS. The home page of our website lists all the technologies supported by Hackolade Studio.
With our polyglot data model, you can define a data structure once, then translate it into a physical data model for any of the technology targets we support. For example, you could derive a physical model each for PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Avro for Kafka, OpenAPI, and Databricks. Or any other combination of target technology for which Hackolade Studio has a plugin.

Metadata-as-Code
Legacy data modeling tools provide, in their enterprise-level edition, their own mart for data models. We think that such an approach is flawed because it creates yet another silo and only gets organizations further away from having a single source-of-truth for collaboration between business and IT stakeholders. No matter how much the vendor may claim that it is "integrated", it is just another metadata repository which, besides holding metadata that is not synchronized elsewhere, requires monitoring, maintenance, backups, upgrades, and additional license fees. Additionally, when it comes to collaboration and versioning, these tools are outdated and very constraining with their centralized control of the check-in/check-out process with users running the risk of being locked out.
At Hackolade, instead of creating yet another siloed repository which would have also required to re-invent the wheel, we reinforce the consolidation of repositories, we concentrate on maximizing synchronization between existing repositories by leveraging Metadata-as-Code, plus we leverage the incredibly reach feature set of proven technology.
With Metadata-as-Code, we mean 3 main principles:
1) co-location of data models with application code in the repo technology that is the most pervasive, and loved by more than 200 million developers worldwide: Git. This co-location means that data models and their schema artifacts follow the same workflow and lifecycle as software evolutions;
2) automation of data modeling operations orchestrated by CI/CD pipelines: forward- and reverse-engineering, format conversions, model comparisons, ALTER scripts generation, documentation generation; synchronization of database environments and across the different metadata receptacles: Git, data catalogs, schema registries, API documentation;
3) publication to business-facing metadata management, data quality and data governance solutions.
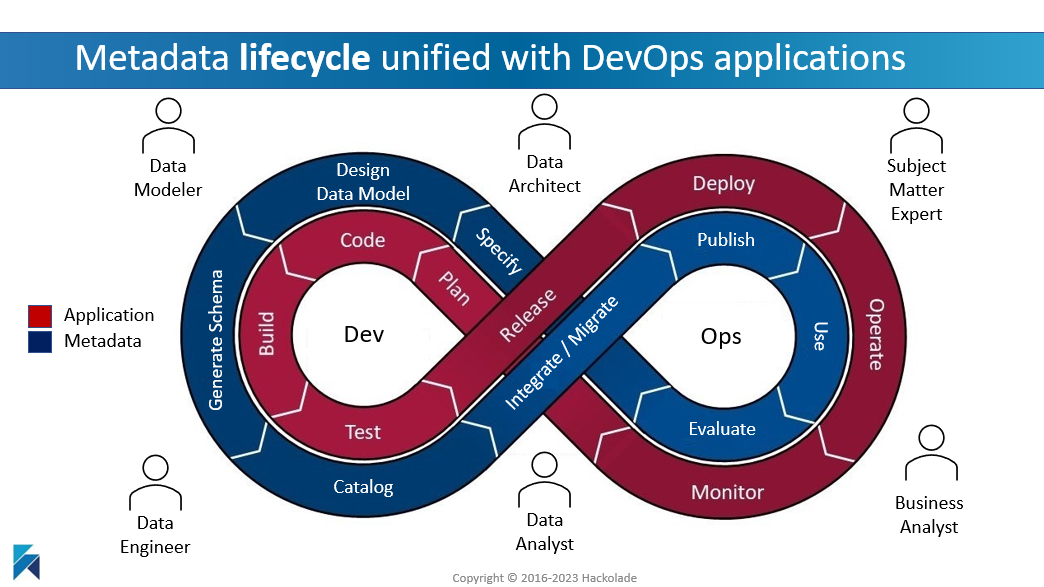
Just like the infinite DevOps loop handles constant iterations for software development lifecycle, the same is true for the evolution of data structures underlying application code for data exchanges and APIs. It is critical for the metadata, through data models and schema contracts, to follow the same lifecycle and keep everything up-to-date.
The business side of human-readable metadata management must be up-to-date and in-sync with the technical side of machine-readable schemas. This process can only work at scale if it is automated. It is hard enough for IT departments to keep in-sync schemas across the various technologies involved in data pipelines. For data to be useful, the business users must have an up-to-date view of the structures, complete with context and meaning.
In terms of features in Hackolade Studio, our Metadata-as-Code strategy leverages:
- the Workgroup Edition native integration with Git repos and platform services (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps Repos) for collaboration, versioning, branching, change tracking, peer reviews, conflict resolution, innersource fork & pull, etc.;
- the Command-Line Interface commands orchestrated by CI/CD pipelines to reverse- and forward-engineer, compare models, generate documentation, etc.;
- our Docker image to run the CLI in multi-threaded parallel jobs;
- our integration with Metadata Management solutions.
Domain-Driven Data Modeling
With our Domain-Driven Data Modeling methodology, we demonstrate that it is possible to strike a balance: not too much data modeling so that it does not get in the way of getting things done, but enough agile data modeling so that business and IT share the same understanding of the context and meaning of data, and so that organizations produce high quality software and data to reach their business objectives.
Domain-Driven Data Modeling is inspired of course by Domain-Driven Design which has been used for 20 years in software development. The principles are simple...
It is not desirable to ignore data modeling because a design-first approach is proven to beat a code-first approach in terms of efficiency, productivity, quality, and total cost of ownership.
But too much data modeling of large and complex models is counter-productive. Everyone has an anecdote about Enterprise Data Models so big that they were obsolete before they were completed, and impossible to understand for humans.
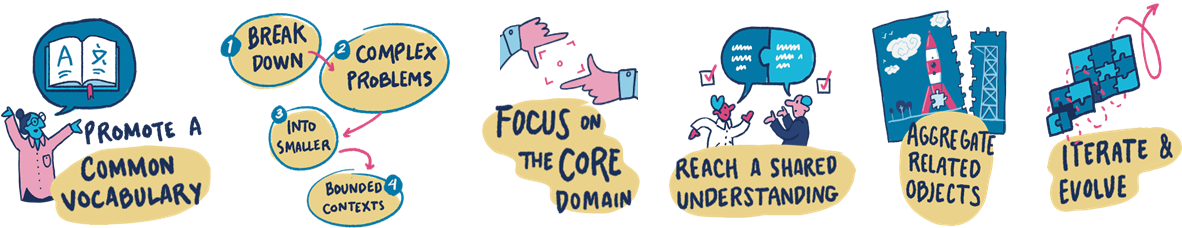
The major principles are:
- break down complex problems into smaller ones
- focus on the core and concentrate efforts for maximum impact
- use data models as a communication tool and help promote a common vocabulary...
- collaborate with subject-matter experts to reach a shared understanding
- cluster together what belongs together with aggregated objects
- iterate and evolve through continuous refinement of the solution
Conclusion
Hackolade Studio provides unique data modeling capabilities: a next-gen platform supporting the needs of modern and agile organizations, the Polyglot method for truly technology-agnostic logical data models, and Metadata-as-Code to provide a single source-of-truth for business and IT. Together with a Domain-Driven Data Modeling methodology, organizations can achieve this vision.
At a tactical level, data modeling serves a design purpose -- the design of data structures used in databases and data exchanges -- and a communication purpose -- the collaborative discussion of these structures between the different stakeholders of data, whether they are from the technical side of the organization, or the business side.
At a more strategic level, the purpose of data modeling is therefore to

This shared understanding of the context and meaning of data allows organizations to make business sense of their data while remaining in compliance with rules and regulations. Hackolade Studio provides a single source-of-truth for business stakeholders (analysts, domain experts) and IT (developers, and data engineers, data architects, data modelers) to synchronize data structures with its context and meaning across technical platforms and data dictionaries or metadata management applications.